🌍 Environmental Studies

Seasons
Seasons are periods of the year with distinct weather patterns. The four main seasons are Spring, Summer, Autumn, and Winter. Each season brings different changes in nature.

Animals
Animals are living beings that move, eat, and reproduce. They live in forests, oceans, deserts, and even our homes. Some animals are wild, and some are domestic.

Pollution
Pollution is the contamination of air, water, or land. It harms humans, animals, and the environment. Reducing waste and using clean energy helps fight pollution.
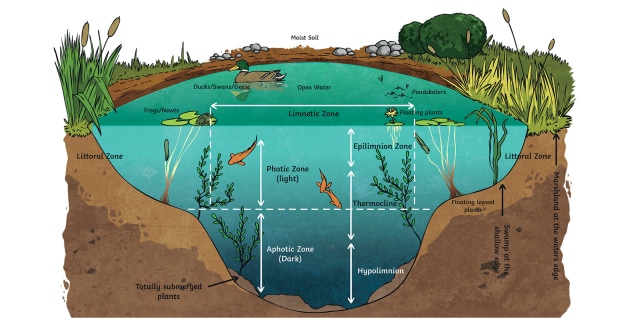
Ecosystems
An ecosystem includes all living things like plants and animals, and their environment. Forests, ponds, and oceans are examples. All parts of an ecosystem work together.

Climate Change
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. It is largely driven by human activities, especially the burning of fossil fuels.

Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variety of life on Earth, including the diversity of species, ecosystems, and genetic variations. It is vital for ecosystem health and resilience.
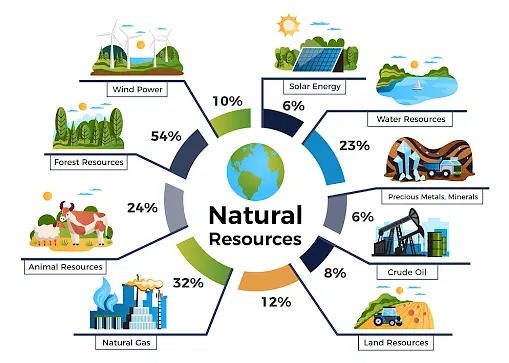
Resource Management
Resource management involves the responsible use and protection of natural resources such as water, soil, and minerals to ensure sustainability.
Impact of Human Activities on Ecosystems
Human activities like deforestation, pollution, and urbanization have significant impacts on ecosystems, often leading to habitat loss and biodiversity decline.

Environmental Policy and Law
Environmental laws and policies are designed to protect natural resources and public health. They include regulations on pollution, conservation, and sustainable development.

Environmental Chemistry
Environmental chemistry studies chemical processes occurring in the environment, focusing on pollutants and their effects on ecosystems and human health.

Geosciences
Geosciences explore Earth’s physical structure, history, and processes. This includes geology, meteorology, oceanography, and soil science.

Social Sciences
Social sciences study human behavior and societies, helping us understand how culture, economics, and politics affect environmental issues and solutions.